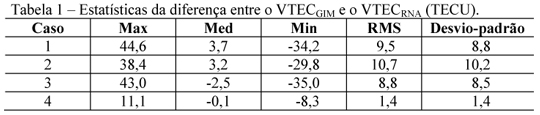
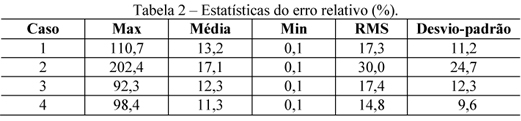
An approach to predict vertical total electron content (VTEC) using multiplayer percetrons (MLP) artificial neural network (ANN) is presented. The models inputs were defined as being the ionospheric pierce point (IPP) positioning and the universal time (UT), while the output is the VTEC. The seasonal and longer period variations of the ionosphere were taken into account by daily training the ANN. Tests were conducted over an area covering Brazil and its vicinity in both high and low solar activity. The ANNs were trained using the previous 72 hours of data from the Global Ionospheric Maps (GIM) produced by the International GNSS Service (IGS). The trained ANNs were used to predict the VTEC to 72 hours (VTEC RNA). Comparisons between VTEC RNA and the VTEC contained into GIM (VTEC GIM) were made. The root mean square (RMS) of the differences between them varied from 1.4 to 10.7 TEC units (TECU). The relative error shows the ANN can correctly predict the VTEC GIM from 70 to 85%.
Artificial Neural Networks; Ionospheric Delay; Ionosphere