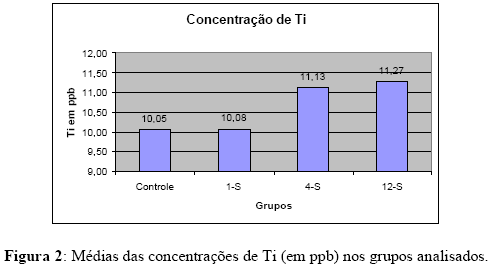
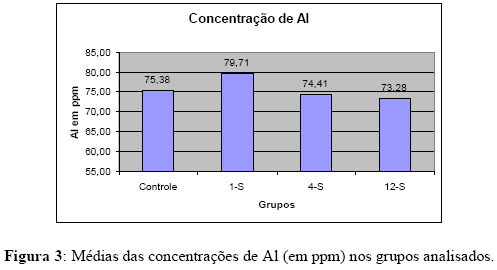
Ti-6Al-4V orthodontic mini-implants may release metallic ions to the human body due to the in vivo corrosion of the alloy in body fluids. The corrosion products can elicit undesirable effects in the human body. The purpose of this study was to measure the concentration of titanium, aluminum, and vanadium in rabbits’ tissues (kidney, liver and lungs) after the insertion of Ti-6Al-4V alloy orthodontic mini-implants. Eighteen New Zealand rabbits had four mini-implants inserted in their left tibia and five rabbits were used as control. After 1, 4, and 12 weeks the rabbits were euthanized, the selected tissues were extracted, and prepared to analysis by graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry. Varied amounts of Ti, Al, and V were detected in the tested groups proving that diffusion of these metals from Ti-6Al-4V orthodontic mini-implants exists. Despite of the tendency of ion release when using the titanium alloy, the amount of metals detected were very low. Then, Ti-6Al-4V orthodontic mini-implants are safe auxiliary orthodontic anchorage devices.
Mini-implants; Ti-6Al-4V; ion release