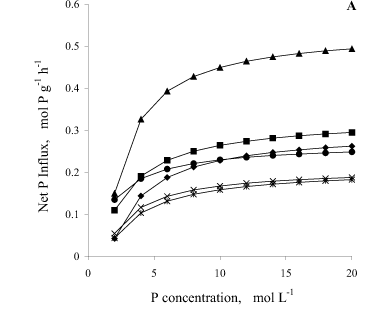
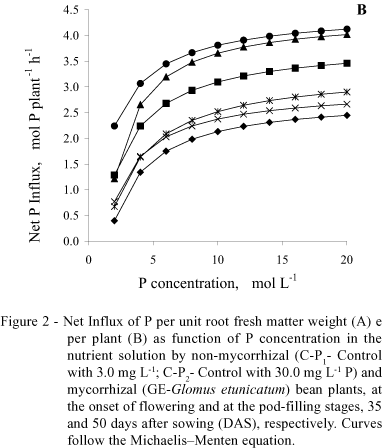
The mechanisms that determine greater P absorption by mycorrhizal plants are still not completely clear, and are attributed, in part, to an increase in the number of absorption sites promoted by the hyphae, and/or to a greater affinity of the colonized hypha or root carriers to P. The effect of mycorrhizae formed by Glomus etunicatum on the kinetic parameters of P absorption by the roots and on P influx in bean plants of the IAC-Carioca cultivar was evaluated, in two distinct plant development periods: at the onset of flowering and at the pod-filling stage (35 and 50 days after sowing, respectively). A mixture of sand and silica (9:1) was utilized as substrate and irrigated with nutrient solution. The kinetics assay was performed by the method of 32P depletion from the solution (depletion curve), using intact plants. Mycorrhization promoted greater growth and P absorption by bean plants, which was more conspicuously observed at the pod-filling stage. Mycorrhizal plants showed higher values of maximum ion uptake rate (Vmax) and net P influx at the flowering stage. Lower minimum ion concentration (Cmin) and Michaelis-Menten constant (Km) values were verified in mycorrhizal plants at the pod-filling stage. Mycorrhizal plants also presented higher net P influx per plant, in both stages. Cmin was the kinetic parameter more intimately related to P absorption, and a significant correlation was obtained between this parameter and shoot P content and accumulation in bean plants.
Phaseolus vulgaris; arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus; absorption kinetics; phosphorus influx; bean